The Surprising Reason Timber Plantations Explode into Megafires
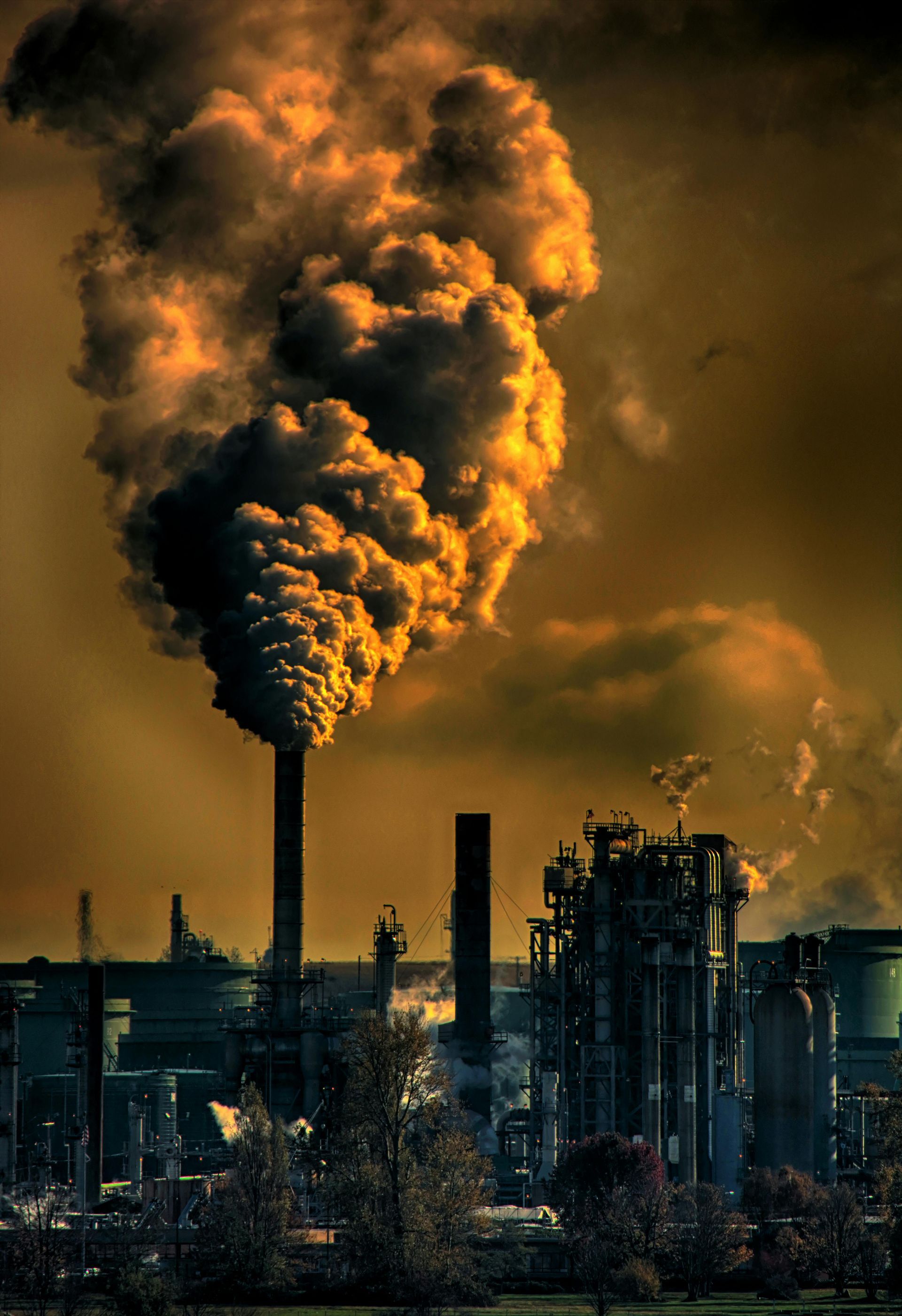
I takt med at de globale temperaturer stiger, og tørkeperioder bliver hyppigere, har fænomenet megabrande – usædvanligt store og ødelæggende skovbrande – fanget verdens opmærksomhed. Mens klimaforandringer og menneskelige aktiviteter ofte får skylden for disse infernoer, er der en anden, mindre omtalt medvirkende faktor: tømmerplantager. Hvad gør disse forvaltede skove særligt modtagelige for at blive voldsomme megabrande? Svaret ligger i deres unikke struktur, artssammensætning og forvaltningspraksis.
Monoculture Vulnerabilities
Tømmerplantager er typisk monokulturer, hvilket betyder, at de kun består af én træart. Denne ensartethed kan føre til et modent miljø for brande. I modsætning til naturlige skove, som ofte kan prale af en bred vifte af arter med varierende niveauer af brandfarlighed og vækstmønstre, mangler monokulturer denne naturlige brandbælte. Når ét træ antændes, kan ilden sprede sig hurtigt over hele plantagen, uhindret af tilstedeværelsen af mindre brandfarlige arter.
Density and Arrangement
The trees in plantations are densely packed to maximize yield, often planted in orderly rows. This setup, while efficient for harvesting, creates a 'tinderbox' effect. The close proximity of trees allows for fires to leap easily from one tree to another. Additionally, the lack of underbrush management leads to the accumulation of combustible material on the forest floor, further enhancing the potential for large-scale fires.
Choice of Species
Valget af træarter i plantager spiller også en nøglerolle. Mange tømmerplantager har hurtigtvoksende arter, såsom fyr eller eukalyptus, som er foretrukne for deres hurtige udbytte i tømmerproduktionen. Disse træer indeholder dog et højt indhold af flygtige olier og harpikser, hvilket gør dem særligt brandfarlige. I tilfælde af brand kan disse træer eksplodere med intensitet og frigive en strøm af strålevarme og gløder.
Fire Suppression Practices
Paradoxically, the very measures intended to prevent fires can also contribute to their severity. Many timber plantations employ rigorous fire suppression efforts, limiting small, manageable fires that could otherwise reduce the buildup of combustible material. Over time, this creates an overload of dry plant matter that turns into a powder keg, ready to ignite with devastating results.
Economic and Policy Considerations
Economic factors and policy decisions also influence the susceptibility of timber plantations to megafires. The drive to maintain production and profit can result in inadequate fire management resources and practices. Moreover, environmental policies sometimes focus on short-term gains without considering long-term ecological balance, allowing conditions favorable to megafires to persist.
Finding Sustainable Solutions
Addressing the megafire threat in timber plantations requires a multidimensional approach. Integrating a diversity of tree species, adopting agroforestry practices, and promoting ecological forestry principles can help create more resilient landscapes. Furthermore, reevaluating fire management policies to include controlled burns and other preventive measures could mitigate the impacts of future fires.
Afslutningsvis kan man sige, at selvom tømmerplantager er designet til produktivitet og vækst, gør de faktorer, der gør dem økonomisk attraktive, dem også modtagelige for katastrofale megabrande. At anerkende og håndtere disse sårbarheder er afgørende for at mindske risikoen for disse massive brande og bevare både vores skove og vores lokalsamfund.
Understanding the Crisis
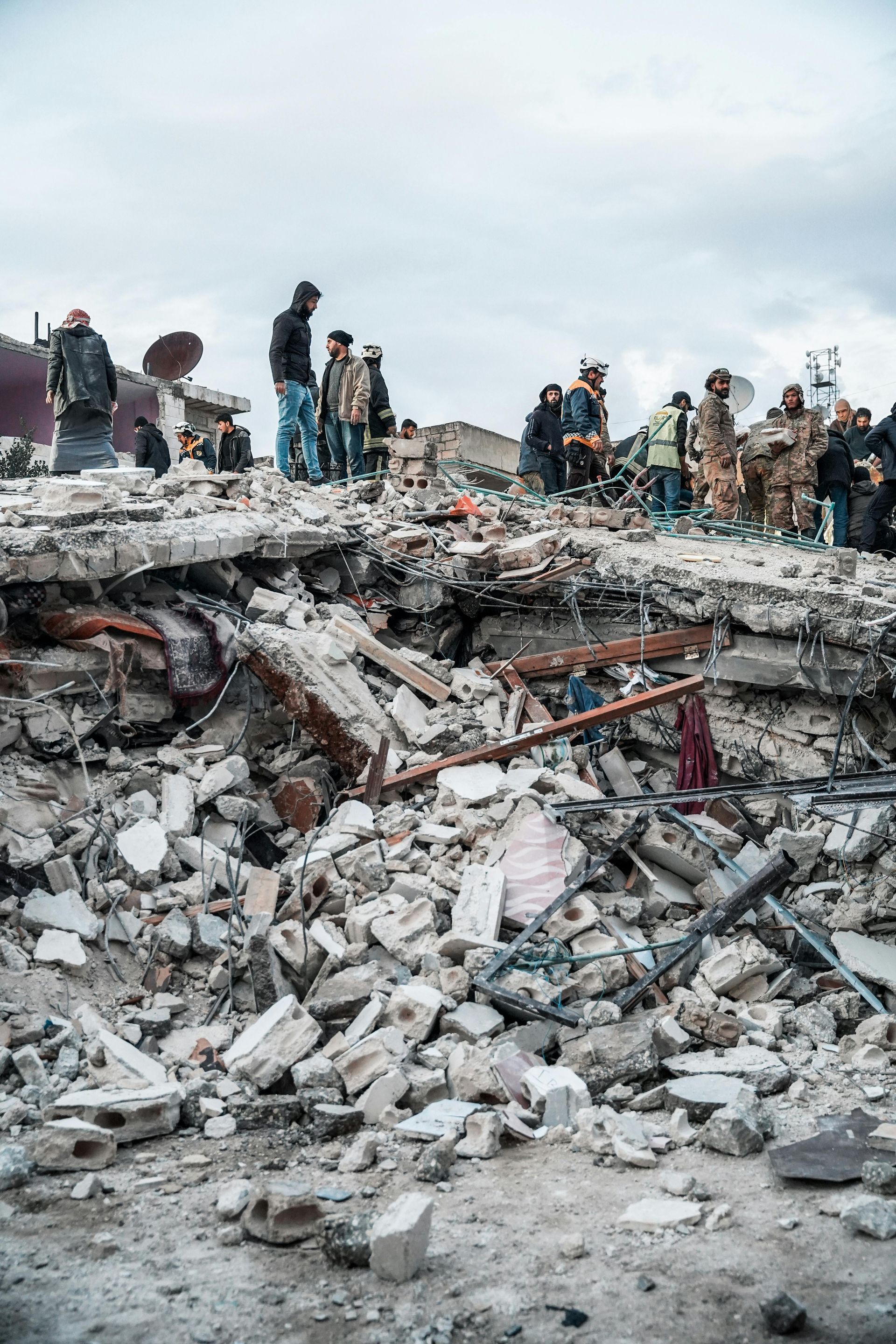
Gaza, en tætbefolket stribe land, der grænser op til Israel og Egypten, har stået over for adskillige vanskeligheder gennem årene. Blokaden, som Israel og Egypten har indført, har i betydelig grad begrænset strømmen af varer og mennesker og dermed lammet den lokale økonomi. Dette har ført til alvorlig mangel på essentielle varer, herunder mad, medicin og elektricitet, hvilket gør dagligdagen yderst vanskelig.
The Impact on Food Security
The blockade, coupled with recurrent conflicts, has devastated Gaza's agriculture and fishing industries, which historically provided sustenance and employed a significant portion of the population. With limited access to arable land and the sea, food production has drastically decreased. Moreover, the destruction of infrastructure has made it exceedingly difficult to store and distribute what little food is available.
The high unemployment rate, hovering around 50%, further exacerbates the situation as families struggle to afford basic necessities. Many rely on international aid to meet their daily food requirements, yet aid deliveries are often disrupted or insufficient to meet the growing needs of the population.
International Efforts and Challenges
Adskillige internationale organisationer arbejder utrætteligt for at yde hjælp og lindre lidelserne i Gaza. FN's Hjælpeorganisation (UNRWA) er sammen med andre NGO'er aktivt involveret i at distribuere fødevarer og yde økonomisk bistand til de mest sårbare samfund. Logistiske udfordringer, mangel på finansiering og politiske begrænsninger hindrer dog ofte disse bestræbelser.
Det internationale samfund står over for udfordringen med at finde balancen mellem humanitær bistand og regionens komplekse geopolitiske realiteter. Bestræbelser på at lette blokaden og fremme udvikling mødes ofte med modstand på grund af sikkerhedsproblemer og politiske uenigheder.
Den menneskelige omkostning
The human cost of the crisis in Gaza is immeasurable. Malnutrition, particularly among children, is a growing concern. According to reports from humanitarian organizations, there is a significant percentage of children suffering from stunted growth and anemia due to poor nutrition. The psychological toll of constant insecurity, limited opportunities, and little hope for the future is profound, affecting the mental well-being of an entire generation.
Vejen fremad
Addressing the issue of starvation in Gaza requires a multifaceted approach. While immediate humanitarian aid is crucial, long-term solutions should focus on lifting the blockade, promoting economic development, and fostering dialogue for a sustainable peace. Collaborative efforts from international governments, local authorities, and NGOs are essential to bring about meaningful change and to restore dignity and self-sufficiency to the people of Gaza.
In conclusion, while the challenge is immense, the global community must not turn a blind eye to the suffering in Gaza. Through concerted efforts, it is possible to alleviate the humanitarian crisis and pave the way for a more stable and prosperous future for the region.